The human body is a marvelous creation. If we scrutinize and look down on all the minor details, we’ll be left spellbound. The harmony with which all the organ systems work together to ensure that the body stays fit and healthy is just wondrous.
Similarly, the whole body is put under stress in a disease state, not only the affected part. If that’s what got you thinking whether gut health causes anxiety, then we’ve got all the answers you need.
What is Gut Health?
In medical terms, our gut, or the gastrointestinal tract, is a series of organs from the mouth to the anus. Collectively, all these organs make up the digestive system. As we know, our gut is responsible for digesting food and making it available for the rest of the body.
But the gastrointestinal system isn’t only responsible for digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and excreting waste. On the contrary, the gut performs some functions that seem entirely unrelated.
For instance, the gut bolsters the body’s immune system and keeps chronic diseases like cancer and diabetes at bay. If you’re a patient of celiac disease, eating gluten can cause abdominal pain and discomfort.
But in some patients, it can also cause candidiasis, dermatitis herpetiformis, dark circles under the eyes, and other non-digestive disorders. So, it is of fundamental importance to understand and maintain proper gut health.
According to doctors and medical experts, our digestive system consists of millions of different types of bacteria. When we usually hear the word bacteria, we think of it as something that can cause diseases and prove harmful.
But the bacteria in our gastrointestinal tract is very different. By birth, the gut microbiome develops a mutualistic relationship with the organs. It helps them perform their functions and gets nutrients and a place to live in return.
Not only that, but gut microbes also play a significant role in the non-digestive functions of our digestive system. A healthy gut ensures the right balance between the bacteria. But poor gut health disrupts that microbiome balance and leads to various medical and neurological issues, including anxiety.
A Detailed Insight into Anxiety
We see a global change when it comes to mental health. A worldwide movement was initiated that promoted and encouraged people to speak up and talk about their emotional battles. Because of this, almost everyone has a gist of what anxiety is. But before we continue with our discussion, let’s take a detailed look at anxiety.
We face potentially harmful and critical conditions in our everyday lives now and then. Our body’s natural reaction to such conditions is worried thoughts, feelings of tension, and several physical changes.
This reaction prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response in the sympathetic nervous system and creates anxiety. Feeling anxious while going to a new job or giving a presentation in class is understandable.

But when this feeling becomes intensified, affecting your day-to-day activities, it may be an anxiety disorder. Living in a constant state of sympathetic response wreaks havoc on your body.
There are numerous mental conditions and emotional disturbances that can cause anxiety. For instance, it is very pronounced in phobias or obsessive-compulsive disorder. People who have post-traumatic stress disorder feel immense anxiety whenever they find themselves in a similar situation.
Patients with heart diseases and thyroid problems often complain about anxiety and stress. But sometimes, the anxiety might be due to a hidden, underlying medical condition. Some tumors malfunction your hormone-producing cells, causing the body to stay in a fight-or-flight condition even without a trigger.
It also may work the other way around. Patients suffering from anxiety disorders often develop some severe diseases. It doesn’t matter if it’s the digestive system, the nervous system, the respiratory system, the immune system, or the cardiovascular system. Your whole body is at risk when you are suffering from anxiety for a prolonged time.
Are Gut Health and Anxiety linked?
Now that we know about gut health and anxiety, let’s talk about how they are linked.
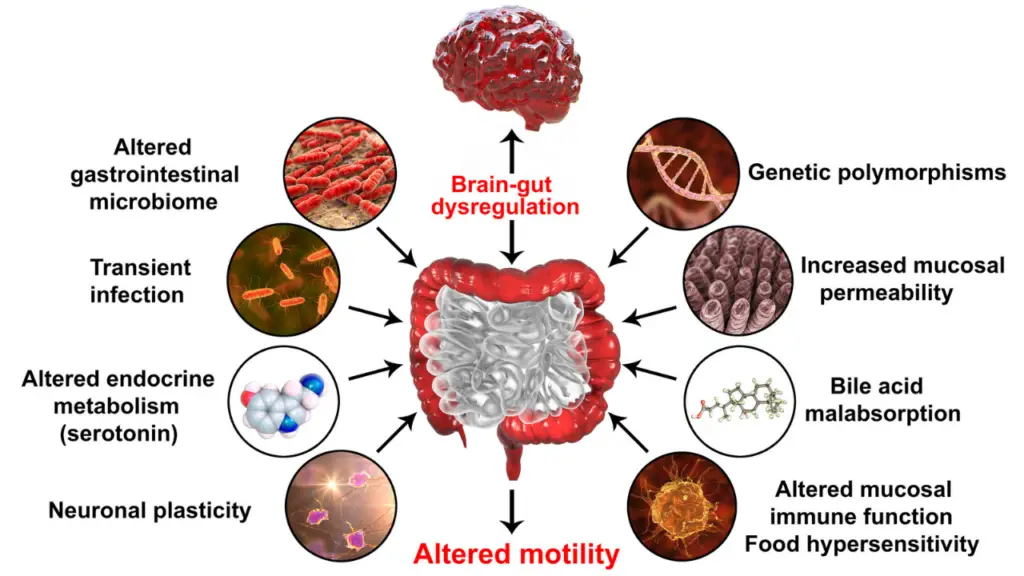
Leaky gut, disturbed microbiome imbalance, and an unhealthy gastrointestinal tract affect mental health and cause anxiety, both directly and indirectly. Here are some ways that explain how that happens:
Release of Harmful Substances
Whenever someone’s gut is damaged, there is a high chance that several harmful substances are released. For instance, in the case of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, the concentration of a chemical called cytokine is elevated.
Then, the cytokine spreads in the blood throughout the body. There is a barrier at the brain’s level that only allows selective chemicals from the blood to pass through. When the cytokines reach the brain, they increase the permeability of this blood-brain barrier.
With this increased permeability, the barrier can no longer keep other harmful substances away from the brain. And when these toxic substances enter the brain, they cause all kinds of mental problems.

Among these neurological conditions, anxiety is the most common one. But some patients have also complained about depression and memory loss.
The elevated levels of cytokines can indirectly cause anxiety as well. The cytokines trigger a small part of the brain that eventually causes the release of a hormone called cortisol. Cortisol is infamous for its stress-inducing property, which causes anxiety and other mental disorders.
The Role of the Vagus Nerve
If you skipped out on biology in high school or forgot what a nerve is, here’s a simple recap. A nerve is a structure that connects the brain or spinal cord to any other part of the body. It can be any part of the body, including the brain and spinal cord as well.
The vagus nerve connects our gut to the brain. In the case of stress, the vagus nerve is stimulated and causes a series of reactions within the gut. Among those, reducing the blood flow and activity of the gut is the most prominent.
But in the opposite scenario, the vagus nerve sends a message to the brain whenever it detects abnormalities. Eventually, normal brain function is affected, and the patient also suffers from anxiety.
Gut Microbiota
The bacteria in the gut that we talked about earlier also prevent anxiety in numerous ways. Let’s discuss each of them.
· They help the local cells of the gut in performing their normal functions. When the number of these bacteria drops, the local cells fail to perform their functions properly. As a result, this creates an imbalance that affects the brain and ultimately leads to anxiety and depression.
· Moreover, gut microbiomes are widely known for their protective role against inflammation. And to top it all, gut bacteria manage to help out the brain cells while sitting in your digestive tract.
· The bacteria produce a compound called butyrate whenever you eat fruits and vegetables. This butyrate defends the gut from inflammation and increases the production of new brain cells. More number of brain cells means healthier and more stable mental health and a lesser chance of anxiety.
· Another way that the gut microbiomes help is by producing some happy hormones. Serotonin and dopamine are two happy hormones that significantly boost mood and reduce anxiety levels. Another hormone called GABA shuts down the stress reactions within the nervous system. And the gut microbiota helps produce all these hormones.
In case of disease or any other factor contributing to an unhealthy gut, these bacteria take the fall too. And when there’s a microbiome imbalance in the gut, the bacteria become helpless and can not perform their functions. Consequently, the patient develops a higher risk for the onset of anxiety and other mental health disorders.
Major Gut Disorders that Cause Anxiety
It is known that gut health influences your mental health and can cause anxiety. Research suggests that anxiety is a common symptom in almost 60 percent of patients with Intestinal Bowel Disease or IBS.

The statistical data from this study confirms the suspicion that anxiety is a typical symptom of IBS. Other than anxiety, the patients with IBS also become more sensitive to emotional disturbances. Indigestion, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain are other major gut disorders that cause anxiety.
The Flip Side
We just discussed how gut health could affect your mental health and lead to anxiety. But does anxiety influence your gut health? If yes, then how?
We talked about the vagus nerve’s role and how it relays messages from the brain to the gut. Under stress conditions, our brain does not function normally. It enters into a sympathetic response, aka fight-or-flight mode, and orders the rest of the body to do so as well.
The vagus nerve is also affected, and it sends a message that restricts the blood flow to the gut. Consequently, the gut activity becomes depressed. If things stay the same way for a longer time, this can seriously impact gut health.
During stress and anxiety, the brain fires up the production of several chemical compounds, including hormones. When the nerves in the gut receive these hormones, they respond with physical symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, and nausea.
You might’ve experienced pain and discomfort in your abdomen whenever you felt anxious or worried. That’s because emotions like stress, depression, and anxiety stimulate chemicals in the brain. These travel down to the gut and activate the pain receptors and signals.
As a result, you become extra sensitive and more aware of even the slightest pain. Many patients complain about increased spasms in the colon that they never feel otherwise. Or, if they were already feeling the pain, the stress increased it significantly.
Some students start eating more whenever their exams are near. In contrast, others lose their appetite and start skipping meals. The first group isn’t avoiding studying by spending more time eating.
And neither is the second group utilizing their mealtimes in productive study hours. Some people lose their appetite because of stress, while others become extra hungry whenever they’re anxious.
Final Words
Your digestive health can affect your mental health and cause anxiety along with other emotional issues. Doctors have come up with various reasons, including microbiome imbalance and the release of harmful substances from the gut.
It is also possible to be the other way around, and it might be your anxiety that’s causing all the gastrointestinal disturbances. For this purpose, you need to take good care of both your gut and mental health. Don’t hesitate to seek the medical and psychological help of a professional if required.






